Ingress
Introduction
- In an earlier chapter, we saw how we can access our deployed containerized application from the external world via Services.
- Among the
ServiceTypestheNodePortandLoadBalancerare the most often used. - For the
LoadBalancer ServiceType, we need to have support from the underlying infrastructure. Even after having the support, we may not want to use it for every Service, asLoadBalancerresources are limited and they can increase costs significantly. - Managing the
NodePort ServiceTypecan also be tricky at times, as we need to keep updating our proxy settings and keep track of theassigned ports. - In this chapter, we will explore the Ingress API resource, which represents another layer of abstraction, deployed in front of the Service API resources, offering a unified method of managing access to our applications from the external world.
Ingress
- With Services, routing rules are associated with a given Service. They exist for as long as the Service exists and there are many rules because there are many Services in the cluster.
- If we can somehow decouple the routing rules from the application and centralize the rules management, we can then update our application without worrying about its external access.
- This can be done using the
Ingressresource. - According to kubernetes.io,
“An Ingress is a collection of rules that allow inbound connections to reach the cluster Services.”
- To allow the inbound connection to reach the cluster Services, Ingress configures a
Layer 7 HTTP/HTTPS load balancerfor Services and provides the following:
- TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Name-based virtual hosting
- Fanout routing
- Loadbalancing
- Custom rules.
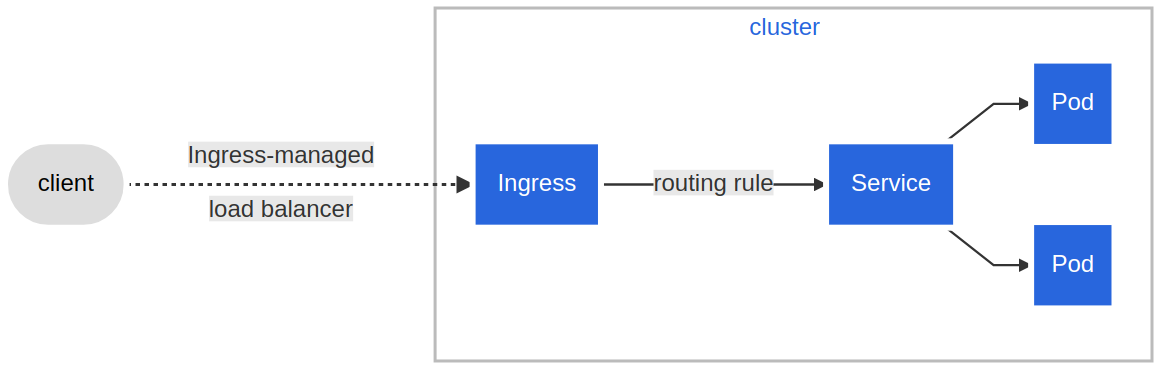
- With Ingress, users do not connect directly to a Service. Users reach the Ingress endpoint, and, from there, the request is forwarded to the desired Service. You can see an example of a
Name-Based Virtual HostingIngress definition below:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: virtual-host-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- host: blue.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: webserver-blue-svc
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- host: green.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: webserver-green-svc
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
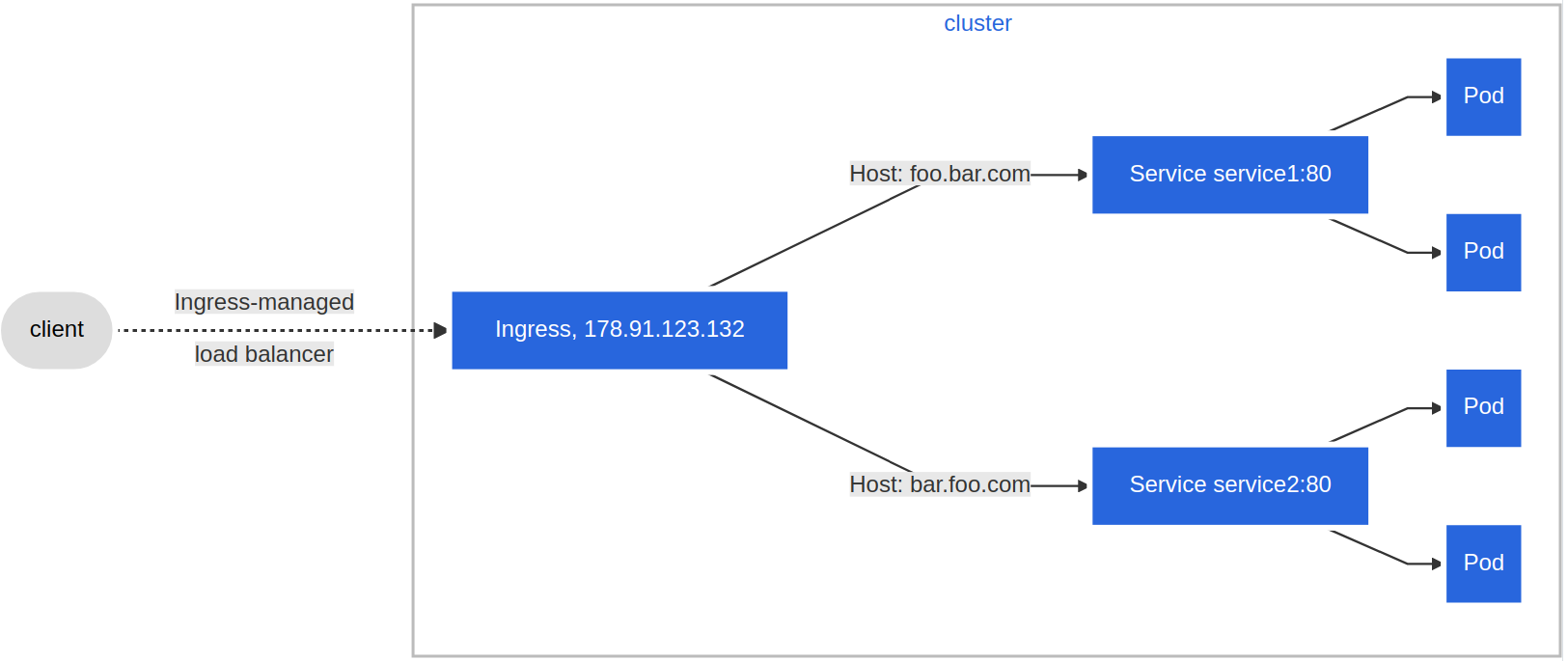
- In the example above, user requests to both
blue.example.comandgreen.example.comwould go to the same Ingress endpoint, and, from there, they would be forwarded towebserver-blue-svc, andwebserver-green-svc, respectively. - Below diagram presents a
Name-Based Virtual HostingIngress rule:
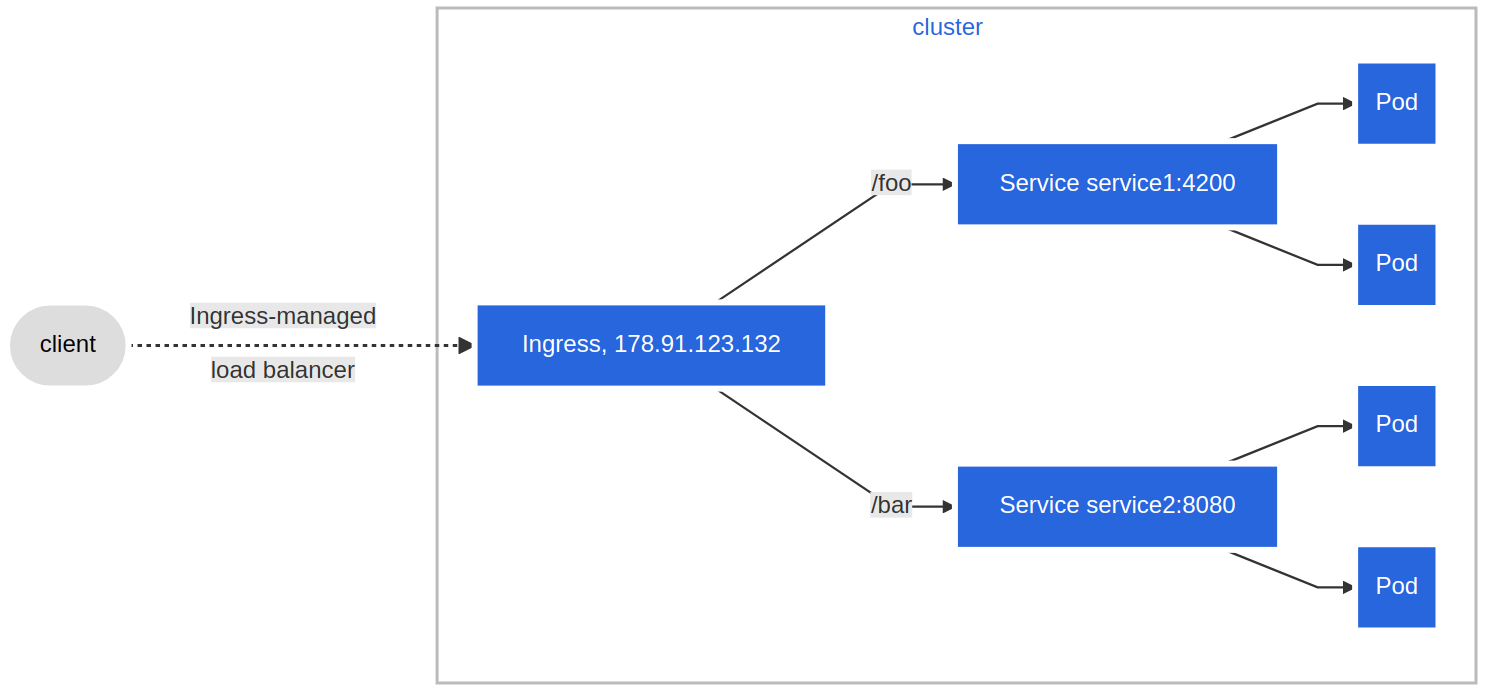
- We can also define Fanout Ingress rules, presented in the example definition and the diagram below, when requests to
example.com/blueandexample.com/greenwould be forwarded towebserver-blue-svcandwebserver-green-svc, respectively:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: fan-out-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /blue
backend:
service:
name: webserver-blue-svc
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- path: /green
backend:
service:
name: webserver-green-svc
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- The Ingress resource does not do any request forwarding by itself, it merely accepts the definitions of traffic routing rules. The ingress is fulfilled by an Ingress Controller, which is a reverse proxy responsible for traffic routing based on rules defined in the Ingress resource.
Ingress Controller
- An Ingress Controller is an application watching the Master Node’s API server for changes in the Ingress resources and updates the Layer 7 Load Balancer accordingly.
- Ingress Controllers are also know as Controllers, Ingress Proxy, Service Proxy, Revers Proxy, etc.
- Kubernetes supports an array of Ingress Controllers, and, if needed, we can also build our own.
- GCE L7 Load Balancer Controller and Nginx Ingress Controller are commonly used Ingress Controllers. Other controllers are Contour, HAProxy Ingress, Istio, Kong, Traefik, etc.
- Starting the Ingress Controller in Minikube is extremely simple.
- Minikube ships with the Nginx Ingress Controller set up as an addon, disabled by default. It can be easily enabled by running the following command:
$ minikube addons enable ingress
Deploy an Ingress Resource
- Once the Ingress Controller is deployed, we can create an Ingress resource using the
kubectl createcommand. - For example, if we create a
virtual-host-ingress.yamlfile with the Name-Based Virtual Hosting Ingress rule definition that we saw in the Ingress section, then we use the following command to create an Ingress resource:
$ kubectl create -f virtual-host-ingress.yaml
Access Services Using Ingress
- With the Ingress resource we just created, we should now be able to access the
webserver-blue-svcorwebserver-green-svcservices using theblue.example.comandgreen.example.comURLs. - As our current setup is on Minikube, we will need to update the host configuration file (
/etc/hostson Mac / Windows / Linux) on our workstation to the Minikube IP for those URLs. - After the update, the file should look similar to:
$ sudo vim /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost
192.168.99.100 blue.example.com green.example.com
- Now we can open
blue.example.comandgreen.example.comon the browser and access each application.
Using Ingress Rules to Access Applications (Demo)
Learning Objectives (Review)
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Explain what Ingress and Ingress Controllers are.
- Understand when to use Ingress.
- Access an application from the external world using Ingress.